Domain Mail Configuration: Understanding SPF, DKIM, DMARC and Confirmation of These Settings can Help to Foil Attackers and Ensure Once Often Received Mass Messages Actually Come from the Authorized People who Sent It
Email usage is an important matter for business communication but also open to cyber criminals. In order to build a security and comfort level of email communication, it is necessary to set up the DNS mail settings in the correct way. In this article, we will discuss the three main technologies used for domain mail configuration: SPF, DKIM, and DMARC set up, and how-to in matter of steps.
What is SPF?
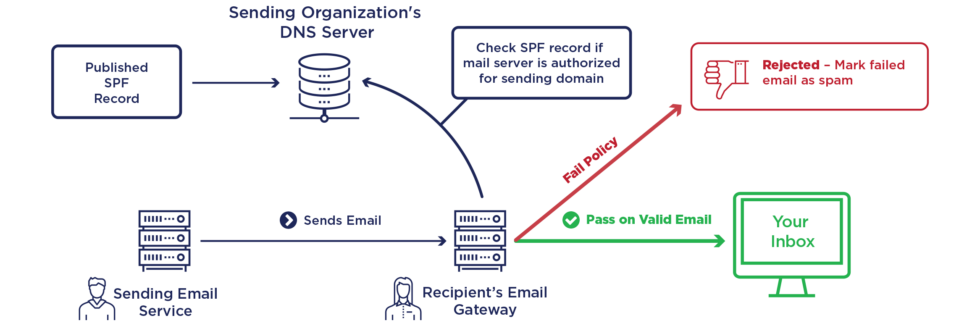
Sender Policy Framework (SPF) is a system where emails are verified so that the sender email is authenticated and the person or entity owning specific IP address gets legitimate platform for email delivery. SPF function enables email domain administrator to give a name to one or more mail servers by assigning an SPF record, indicating that sender’s IP address persued emails are originated from these mail servers. In DNS, the SPF records are defined in the DNS records of a domain and are checked by the mail exchanger to confirm that the email message is legitimate.
How to Configure SPF?
To configure SPF for your domain, follow these steps: To configure SPF for your domain, follow these steps:
Enabled automatic domain name registration or the sign-in to your hosting service provider account.
Find the DNS settings for your domain and look for the TXT record you want to add.
Add a new TXT record with the following information:Add a new TXT record with the following information:
Name/Host/Alias: Write the domain name down or just leave it if you need. From learners of all ages to professionals and researchers, online courses have emerged as a powerful tool for knowledge dissemination and skill acquisition.
Value/Answer/Destination: The correct SPF record format for your domain is “v=spf1 include:example.com ~all” that includes your domain name where example.com is replaced.
TTL: Input the time-living at the end of the record. The customary value is set at 3600 seconds:
Apply the changes by clicking the Save button and then wait for the DNS record to be propagated.
What is DKIM?
The domain keys identified mail (DKIM) is an email authentication technique that is supported by the digital signature thus protecting messages from being misrepresented. DKM is an extension, which is digital signature being into the email header can be verified by recipient’s mail server. DKIM is a signature technique which employs a public and private key pair for signing email messages.
How to Configure DKIM?
To configure DKIM for your domain, follow these steps:To configure DKIM for your domain, follow these steps:
Generate a DKIM key pair. DKIM (DomainKeys Identified Mail) is an authentication protocol used to prevent email spoofing. An online tool such as a DKIM key generator could be used.
Include a DKIM record to your domain algorithm. The DKIM record is composed of a public key used to authenticate the digital signatures. The domain selector and part syntax for the record would be “_selector._domainkey.example.com”; replace selector and example.com values with your own.
Add the header of the email which includes DKIM signature. By employing a DKIM-friendly email client or through a DKIM signing service, domain owners can ensure this takes place.
What is DMARC?
The main aim of DMARC domain-based message authentication, reporting and conformance, is the protection of email spoofing and phishing. DMARC powers the SPF and DKIM features, so it can offer security solutions for all email transmission aspects. DMARC allows domain owners to specify whether their email messages that fail to authenticate should be placed in a quarantine or flagged as spam and seemingly legitimate messages that failed to authenticate would be recognized as spoofs.
How to Configure DMARC?
To configure DMARC for your domain, follow these steps:To configure DMARC for your domain, follow these steps:
Develop a DMARC record in your hosting service’s DNS record. The DMARC record provides information about what processing to apply to emails that cannot be validated via authentication.
Create provisions for failed emails policy. The option of either rejection, quarantine or monitoring of emails that fail authentication test can be asserted upon.
Configure email reporting. DMARC is configurable in a way in a way while it can send reports on the email authentication results.
Therefore, setting SPF, DKIM and DMARC on your domain is what will ensure the safety of email communication between you and your recipients. The steps you will need to follow to tailor these systems to your email domain are discussed in the article which will help keep your email communication from cybercriminals.